之前使用I.MX6Q/I.MX6Q(imx_3.0.35_4.1.0), 1GB RGMII 以太網測試性能大概 495Mbits/sec, 如下是iperf測試過程。
iperf -c 192.168.0.112-u -b 800M -t 10 -l 1000
Client connecting to 192.168.112.125, UDP port 5002
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
[ 3] local 192.168.112.6 port 45230 connected with 192.168.112.125 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 0.0-10.0 sec 590 MBytes 495 Mbits/sec
[ 3] Sent 618437 datagrams
[ 3] WARNING: did not receive ack of last datagram after 10 tries.
讀勘誤手冊 "Chip Errata for the i.MX 6",里面有如下描述ERR004512:
IMX6DQCE (nxp.com.cn) 確實和測試比較吻合。

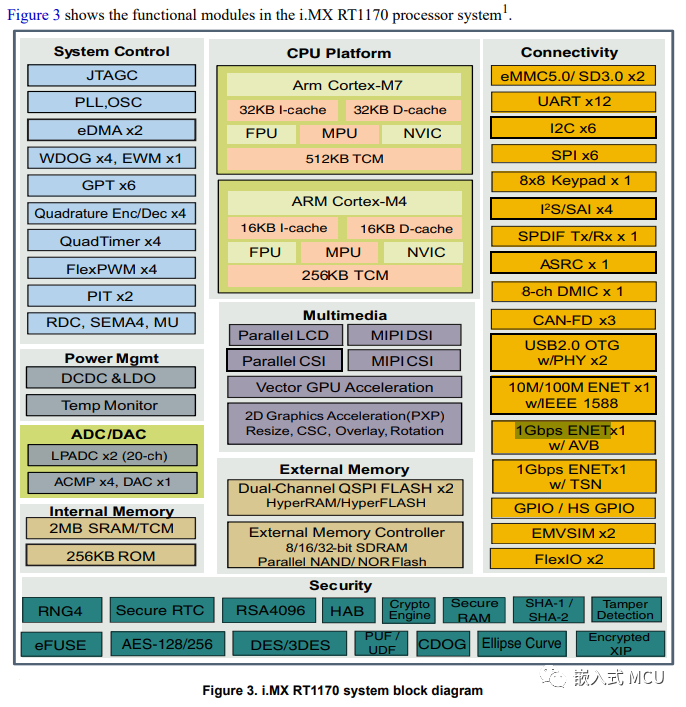
目前使用 MIMXRT1176AVM8A MCU 芯片內置的1G 以太網。
為了驗證網絡性能,使用Iperf 吞吐性能測試如下:硬件電路板——MIMXRT1170-EVK C2,軟件包—— SDK_2.12.0-MIMXRT1170-EVK,下載鏈接如下。添加 iperf 代碼到 lwip_ping_freertos_cm7中,使用flexspi nor sdram 調試。
lwipopts.h文件需要做如下配置才能達到比較高的網絡速率,如下是測試結果。
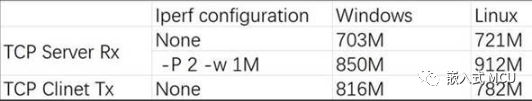
這些結果不完全相同,與主機操作系統也存在性能差異,不同的主機性能也存在顯著差異。總體來講 MIMXRT1176 MCU的 1G網絡性能是沒有I.MX6上面的速率限制的問題。
lwipopts.h 配置文件如下:
/** @file lwipopts.h
* This file is based on srcincludelwipopt.h*/
#ifndef __LWIPOPTS_H__
#define __LWIPOPTS_H__
#include "fsl_device_registers.h"
#if USE_RTOS
/*SYS_LIGHTWEIGHT_PROT==1: if you want inter-task protection for certain critical regions during buffer allocation, deallocation and memoryallocation and deallocation. */
#define SYS_LIGHTWEIGHT_PROT 1
/*NO_SYS==0: Use RTOS */
#define NO_SYS 0
/*LWIP_NETCONN==1: Enable Netconn API (require to use api_lib.c)*/
#define LWIP_NETCONN 1
/** LWIP_SOCKET==1: Enable Socket API (require to use sockets.c)*/
#define LWIP_SOCKET 1
/**LWIP_SO_RCVTIMEO==1: Enable receive timeout for sockets/netconns andSO_RCVTIMEO processing.*/
#define LWIP_SO_RCVTIMEO 1
#else
/** NO_SYS==1: Bare metal lwIP*/
#define NO_SYS 1
/*LWIP_NETCONN==0: Disable Netconn API (require to use api_lib.c)*/
#define LWIP_NETCONN 0
/** LWIP_SOCKET==0: Disable Socket API (require to use sockets.c)*/
#define LWIP_SOCKET 0
/** LWIP_ALLOW_MEM_FREE_FROM_OTHER_CONTEXT=1: we need to free PBUF_RAM pbufsfrom ISR context on LPC.*/
#if defined(FSL_FEATURE_SOC_LPC_ENET_COUNT) && (FSL_FEATURE_SOC_LPC_ENET_COUNT > 0)
#ifndef LWIP_ALLOW_MEM_FREE_FROM_OTHER_CONTEXT
#define LWIP_ALLOW_MEM_FREE_FROM_OTHER_CONTEXT 1
#endif
#endif
#endif
/* ---------- Core locking ---------- */
void sys_check_core_locking(void);
#define LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED() sys_check_core_locking()
/* ---------- Memory options ---------- */
/**
* MEM_ALIGNMENT: should be set to the alignment of the CPU
* 4 byte alignment -> #define MEM_ALIGNMENT 4
* 2 byte alignment -> #define MEM_ALIGNMENT 2
*/
#ifndef MEM_ALIGNMENT
#define MEM_ALIGNMENT 4
#endif
/**
* MEM_SIZE: the size of the heap memory. If the application will send
* a lot of data that needs to be copied, this should be set high.
*/
#ifndef MEM_SIZE
#define MEM_SIZE (22 * 1024)
#endif
/* MEMP_NUM_PBUF: the number of memp struct pbufs. If the applicationsends a lot of data out of ROM (or other static memory), this should be set high. */
#ifndef MEMP_NUM_PBUF
#define MEMP_NUM_PBUF ((TCP_WND + TCP_SND_BUF) / TCP_MSS)//15
#endif
/* MEMP_NUM_UDP_PCB: the number of UDP protocol control blocks. Oneper active UDP "connection". */
#ifndef MEMP_NUM_UDP_PCB
#define MEMP_NUM_UDP_PCB 6
#endif
/* MEMP_NUM_TCP_PCB: the number of simulatenously active TCP
connections. */
#ifndef MEMP_NUM_TCP_PCB
#define MEMP_NUM_TCP_PCB 10
#endif
/* MEMP_NUM_TCP_PCB_LISTEN: the number of listening TCP
connections. */
#ifndef MEMP_NUM_TCP_PCB_LISTEN
#define MEMP_NUM_TCP_PCB_LISTEN 6
#endif
/* MEMP_NUM_TCP_SEG: the number of simultaneously queued TCP
segments. */
#ifndef MEMP_NUM_TCP_SEG
#define MEMP_NUM_TCP_SEG ((3 * TCP_SND_BUF) / TCP_MSS + 1)//22
#endif
/* MEMP_NUM_SYS_TIMEOUT: the number of simulateously active
timeouts. */
#ifndef MEMP_NUM_SYS_TIMEOUT
#define MEMP_NUM_SYS_TIMEOUT 10
#endif
/* ---------- Pbuf options ---------- */
/* PBUF_POOL_SIZE: the number of buffers in the pbuf pool. */
#ifndef PBUF_POOL_SIZE
#define PBUF_POOL_SIZE 20//9
#endif
/* PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE: the size of each pbuf in the pbuf pool. */
/* Default value is defined in lwipsrcincludelwipopt.h as
LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(TCP_MSS+40+PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN+PBUF_LINK_HLEN)*/
/* ---------- TCP options ---------- */
#ifndef LWIP_TCP
#define LWIP_TCP 1
#endif
#ifndef TCP_TTL
#define TCP_TTL 255
#endif
/* Controls if TCP should queue segments that arrive out of
order. Define to 0 if your device is low on memory. */
#ifndef TCP_QUEUE_OOSEQ
#define TCP_QUEUE_OOSEQ 0
#endif
/* TCP Maximum segment size. */
#ifndef TCP_MSS
#define TCP_MSS (1500 - 40) /* TCP_MSS = (Ethernet MTU - IP header size - TCP header size) */
#endif
/* TCP sender buffer space (bytes). */
#ifndef TCP_SND_BUF
#define TCP_SND_BUF (40 * TCP_MSS)//(6 * TCP_MSS) // 2
#endif
/* TCP sender buffer space (pbufs). This must be at least = 2 *
TCP_SND_BUF/TCP_MSS for things to work. */
#ifndef TCP_SND_QUEUELEN
#define TCP_SND_QUEUELEN (3 * TCP_SND_BUF) / TCP_MSS // 6
#endif
/* TCP receive window. */
#ifndef TCP_WND
#define TCP_WND (20 * TCP_MSS)//(2 * TCP_MSS)
#endif
/* Enable backlog*/
#ifndef TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG
#define TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG 1
#endif
/* ---------- ICMP options ---------- */
#ifndef LWIP_ICMP
#define LWIP_ICMP 1
#endif
/* ---------- DHCP options ---------- */
/* Enable DHCP module. */
#ifndef LWIP_DHCP
#define LWIP_DHCP 1
#endif
/* ---------- UDP options ---------- */
#ifndef LWIP_UDP
#define LWIP_UDP 1
#endif
#ifndef UDP_TTL
#define UDP_TTL 255
#endif
/* ---------- Statistics options ---------- */
#ifndef LWIP_STATS
#define LWIP_STATS 0
#endif
#ifndef LWIP_PROVIDE_ERRNO
#define LWIP_PROVIDE_ERRNO 1
#endif
/*---------- Checksum options ----------
*/
/*Some MCU allow computing and verifying the IP, UDP, TCP and ICMP checksums by hardware:
- To use this feature let the following define uncommented.
- To disable it and process by CPU comment the the checksum.
*/
//#define CHECKSUM_BY_HARDWARE
#ifdef CHECKSUM_BY_HARDWARE
/* CHECKSUM_GEN_IP==0: Generate checksums by hardware for outgoing IP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_GEN_IP 0
/* CHECKSUM_GEN_UDP==0: Generate checksums by hardware for outgoing UDP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_GEN_UDP 0
/* CHECKSUM_GEN_TCP==0: Generate checksums by hardware for outgoing TCP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_GEN_TCP 0
/* CHECKSUM_CHECK_IP==0: Check checksums by hardware for incoming IP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_CHECK_IP 0
/* CHECKSUM_CHECK_UDP==0: Check checksums by hardware for incoming UDP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_CHECK_UDP 0
/* CHECKSUM_CHECK_TCP==0: Check checksums by hardware for incoming TCP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_CHECK_TCP 0
#else
/* CHECKSUM_GEN_IP==1: Generate checksums in software for outgoing IP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_GEN_IP 1
/* CHECKSUM_GEN_UDP==1: Generate checksums in software for outgoing UDP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_GEN_UDP 1
/* CHECKSUM_GEN_TCP==1: Generate checksums in software for outgoing TCP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_GEN_TCP 1
/* CHECKSUM_CHECK_IP==1: Check checksums in software for incoming IP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_CHECK_IP 1
/* CHECKSUM_CHECK_UDP==1: Check checksums in software for incoming UDP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_CHECK_UDP 1
/* CHECKSUM_CHECK_TCP==1: Check checksums in software for incoming TCP packets.*/
#define CHECKSUM_CHECK_TCP 1
#endif
/*DEFAULT_THREAD_STACKSIZE: The stack size used by any other lwIP thread.The stack size value itself is platform-dependent, but is passed tosys_thread_new() when the thread is created.*/
#ifndef DEFAULT_THREAD_STACKSIZE
#define DEFAULT_THREAD_STACKSIZE 3000
#endif
/*DEFAULT_THREAD_PRIO: The priority assigned to any other lwIP thread.The priority value itself is platform-dependent, but is passed tosys_thread_new() when the thread is created.*/
#ifndef DEFAULT_THREAD_PRIO
#define DEFAULT_THREAD_PRIO 3
#endif
#define LWIP_DEBUG
#ifdef LWIP_DEBUG
#define U8_F "c"
#define S8_F "c"
#define X8_F "02x"
#define U16_F "u"
#define S16_F "d"
#define X16_F "x"
#define U32_F "u"
#define S32_F "d"
#define X32_F "x"
#define SZT_F "u"
#endif
#define TCPIP_MBOX_SIZE 32
#define TCPIP_THREAD_STACKSIZE 1024
#define TCPIP_THREAD_PRIO 8
/*DEFAULT_RAW_RECVMBOX_SIZE: The mailbox size for the incoming packets on aNETCONN_RAW. The queue size value itself is platform-dependent, but is passedto sys_mbox_new() when the recvmbox is created.*/
#define DEFAULT_RAW_RECVMBOX_SIZE 12
/*DEFAULT_UDP_RECVMBOX_SIZE: The mailbox size for the incoming packets on aNETCONN_UDP. The queue size value itself is platform-dependent, but is passedto sys_mbox_new() when the recvmbox is created.*/
#define DEFAULT_UDP_RECVMBOX_SIZE 12
/*DEFAULT_TCP_RECVMBOX_SIZE: The mailbox size for the incoming packets on aNETCONN_TCP. The queue size value itself is platform-dependent, but is passedto sys_mbox_new() when the recvmbox is created. */
#define DEFAULT_TCP_RECVMBOX_SIZE 12
/**DEFAULT_ACCEPTMBOX_SIZE: The mailbox size for the incoming connections.The queue size value itself is platform-dependent, but is passed tosys_mbox_new() when the acceptmbox is created.*/
#define DEFAULT_ACCEPTMBOX_SIZE 12
#if (LWIP_DNS || LWIP_IGMP || LWIP_IPV6) && !defined(LWIP_RAND)
/* When using IGMP or IPv6, LWIP_RAND() needs to be defined to a random-function returning an u32_t random value*/
#include "lwip/arch.h"
u32_t lwip_rand(void);
#define LWIP_RAND() lwip_rand()
#endif
#endif /* __LWIPOPTS_H__ */
/*****END OF FILE****/
審核編輯:湯梓紅
-
mcu
+關注
關注
146文章
17317瀏覽量
352640 -
以太網
+關注
關注
40文章
5460瀏覽量
172726 -
性能測試
+關注
關注
0文章
214瀏覽量
21389
原文標題:MIMXRT1176AVM8A 1G 以太網網絡性能測試
文章出處:【微信號:嵌入式 MCU,微信公眾號:嵌入式 MCU】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
為什么ML402以太網1G傳輸時只有led100是綠色?
是否可以用MIMXRT117H替換MIMXRT1176?
從MIMXRT1176DVMAA更改為MIMXRT1176AVM8A時出現的問題怎么解決?
BLADE和Voltaire推出高密度10Gb以太網網絡方案
基于SOPC技術的嵌入式以太網網絡終端設備解決方案設計詳解




 MIMXRT1176AVM8A 1G以太網網絡性能測試
MIMXRT1176AVM8A 1G以太網網絡性能測試











評論