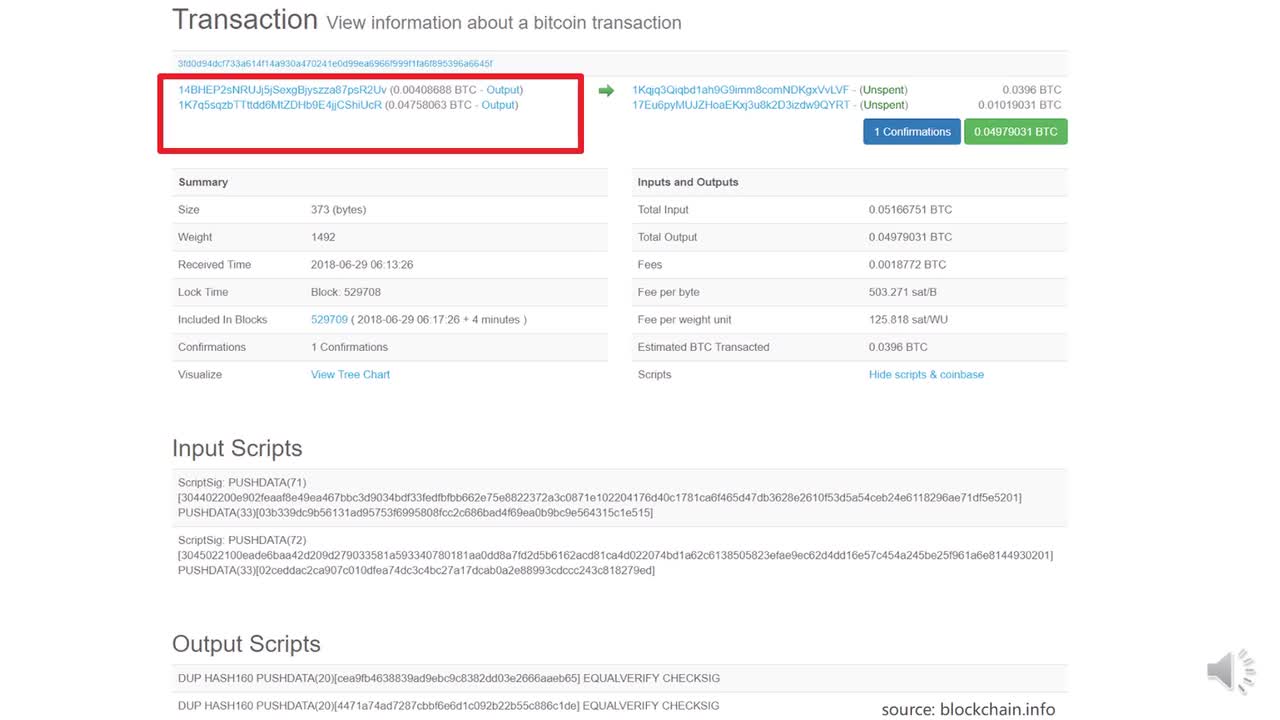
區塊鏈原本是比特幣等加密貨幣存儲數據的一種獨特方式,是一種自引用的數據結構,用來存儲大量交易信息,每條記錄從后向前有序鏈接起來,具備公開透明、無法篡改、方便追溯的特點。實際上,這種特性也直接體現了整個比特幣的特點,因此使用區塊鏈來概括加密貨幣背后的技術實現是非常直觀和恰當的。區塊鏈是一項技術,加密貨幣是其開發實現的一類產品(含有代幣,也有不含代幣的區塊鏈產品),不能等同或混淆。與加密貨幣相比,區塊鏈這個名字拋開了代幣的概念,更加形象化、技術化、去政治化,更適合作為一門技術去研究、去推廣。
區塊鏈基礎架構模型
一般說來,區塊鏈系統由數據層、網絡層、共識層、激勵層、合約層和應用層組成。 其中,數據層封裝了底層數據區塊以及相關的數據加密和時間戳等技術;網絡層則包括分布式組網機制、數據傳播機制和數據驗證機制等;共識層主要封裝網絡節點的各類共識算法;激勵層將經濟因素集成到區塊鏈技術體系中來,主要包括經濟激勵的發行機制和分配機制等;合約層主要封裝各類腳本、算法和智能合約,是區塊鏈可編程特性的基礎;應用層則封裝了區塊鏈的各種應用場景和案例。該模型中,基于時間戳的鏈式區塊結構、分布式節點的共識機制、基于共識算力的經濟激勵和靈活可編程的智能合約是區塊鏈技術最具代表性的創新點。

區塊鏈代碼實現
哈希樹的跟節點稱為Merkle根,Merkle樹可以僅用log2(N)的時間復雜度檢查任何一個數據元素是否包含在樹中:
package test;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MerkleTrees {
// transaction List
List《String》 txList;
// Merkle Root
String root;
/**
* constructor
* @param txList transaction List 交易List
*/
public MerkleTrees(List《String》 txList) {
this.txList = txList;
root = “”;
}
/**
* execute merkle_tree and set root.
*/
public void merkle_tree() {
List《String》 tempTxList = new ArrayList《String》();
for (int i = 0; i 《 this.txList.size(); i++) {
tempTxList.add(this.txList.get(i));
}
List《String》 newTxList = getNewTxList(tempTxList);
while (newTxList.size() != 1) {
newTxList = getNewTxList(newTxList);
}
this.root = newTxList.get(0);
}
/**
* return Node Hash List.
* @param tempTxList
* @return
*/
private List《String》 getNewTxList(List《String》 tempTxList) {
List《String》 newTxList = new ArrayList《String》();
int index = 0;
while (index 《 tempTxList.size()) {
// left
String left = tempTxList.get(index);
index++;
// right
String right = “”;
if (index != tempTxList.size()) {
right = tempTxList.get(index);
}
// sha2 hex value
String sha2HexValue = getSHA2HexValue(left + right);
newTxList.add(sha2HexValue);
index++;
}
return newTxList;
}
/**
* Return hex string
* @param str
* @return
*/
public String getSHA2HexValue(String str) {
byte[] cipher_byte;
try{
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance(“SHA-256”);
md.update(str.getBytes());
cipher_byte = md.digest();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(2 * cipher_byte.length);
for(byte b: cipher_byte) {
sb.append(String.format(“%02x”, b&0xff) );
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return “”;
}
/**
* Get Root
* @return
*/
public String getRoot() {
return this.root;
}
}
數據準備
我們將交易的數據,放入到List中:
List《String》 tempTxList = new ArrayList《String》();
tempTxList.add(“a”);
tempTxList.add(“b”);
tempTxList.add(“c”);
tempTxList.add(“d”);
tempTxList.add(“e”);123456
實現過程
準備交易數據
計算出每個數據的hash值,從左到右逐步組成樹的左右節點
執行循環知道最后只剩下一個數據
97
private List《String》 getNewTxList(List《String》 tempTxList) {
List《String》 newTxList = new ArrayList《String》();
int index = 0;
while (index 《 tempTxList.size()) {
// left
String left = tempTxList.get(index);
index++;
// right
String right = “”;
if (index != tempTxList.size()) {
right = tempTxList.get(index);
}
// sha2 hex value
String sha2HexValue = getSHA2HexValue(left + right);
newTxList.add(sha2HexValue);
index++;
}123456789101112131415161718
測試
package test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class App {
public static void main(String [] args) {
List《String》 tempTxList = new ArrayList《String》();
tempTxList.add(“a”);
tempTxList.add(“b”);
tempTxList.add(“c”);
tempTxList.add(“d”);
tempTxList.add(“e”);
MerkleTrees merkleTrees = new MerkleTrees(tempTxList);
merkleTrees.merkle_tree();
System.out.println(“root : ” + merkleTrees.getRoot());
}
}
執行結果
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App









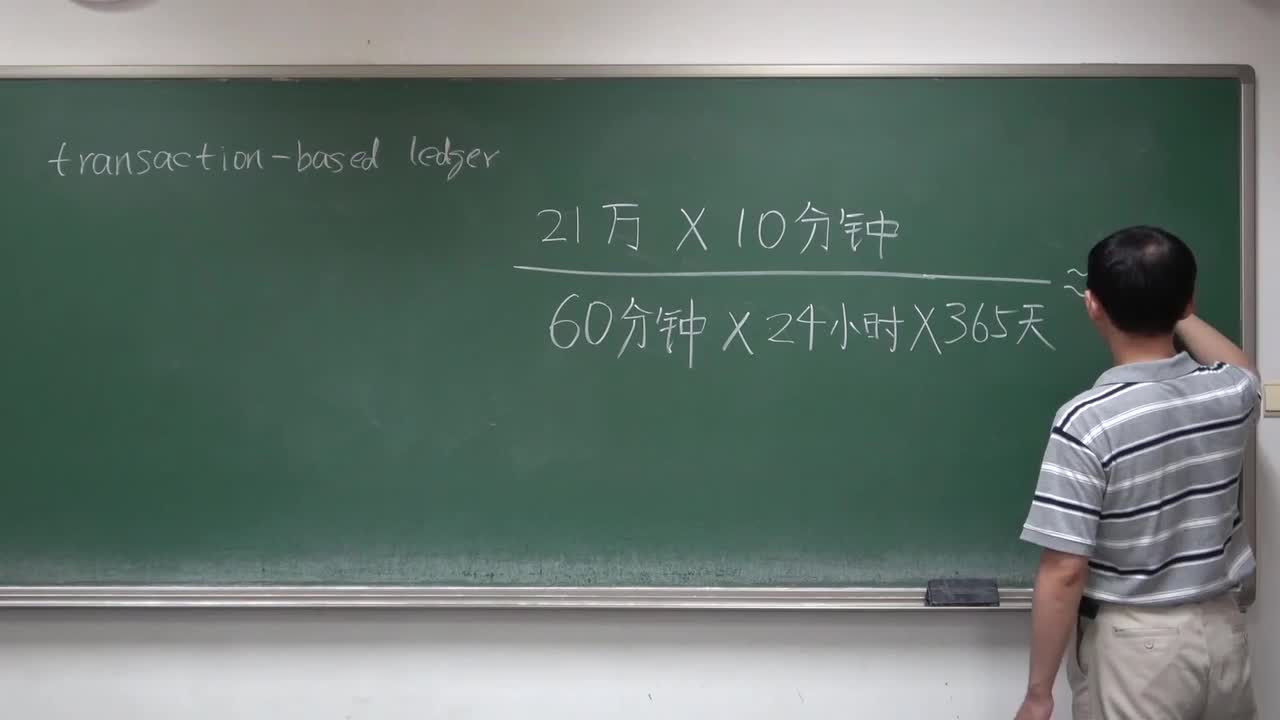














評論